What is Data Preprocessing? Definition, Concepts, Importance, Tools (2025)
Data scientists spend around 60% of their time preprocessing data, which highlights how crucial it is for converting data into actionable insights. Data preprocessing plays a critical role in enhancing the reliability and accuracy of analytics.
But imagine if that 60% could be reduced to 10%. What if instead of learning complex preprocessing workflows, you could simply tell your data what to do in plain English?
This blog will discuss why data preprocessing is essential for making data suitable for comprehensive analysis. We’ll also explore how conversational AI is democratizing data preprocessing, making it accessible to everyone—not just data scientists with advanced technical skills.
What is Data Preprocessing?
Data preprocessing is the critical first step in analyzing data. It lets you transform raw data into an understandable and usable format for analysis. It’s a comprehensive process that ensures the data is primed and ready for the subsequent exploration, modeling, and interpretation stages.
Traditional data preprocessing requires extensive technical knowledge, complex tool configurations, and hours of manual work. However, conversational AI is revolutionizing this process by allowing users to describe their preprocessing needs in natural language, making sophisticated data transformation accessible to business users, analysts, and domain experts without deep technical expertise.
While data preprocessing must be performed before building machine learning (ML) models, it’s not the only step that precedes analytics. Here’s how these steps differ:
Data Cleaning vs. Data Preprocessing
While often used interchangeably, data cleaning and data preprocessing are not the same.
Data cleaning is a subset of preprocessing, primarily concerned with identifying and correcting errors and inconsistencies within the dataset.
Data preprocessing, on the other hand, is an umbrella term that includes data cleaning and other processes such as normalization, transformation, and feature extraction, which are essential to prepare data for analysis.
Data Exploration vs. Data Preprocessing
Data exploration is like detective work, where you look for patterns, anomalies, and insights within the data. It involves asking questions and getting answers through visual and quantitative methods.
Data preprocessing, however, is the groundwork that makes such exploration possible. It involves cleaning, transforming, and organizing data to be effectively explored and analyzed for meaningful insights.
Data Preparation vs Data Preprocessing
Data preparation and data preprocessing are often used synonymously, but they can have different connotations.
Data preparation can be a broader category, including preprocessing, data collection, and integration. It encompasses the entire process of getting data ready for analysis, from when it’s gathered to when it’s fed into analytical tools.
Data preprocessing, while part of the preparation, is specifically focused on transforming and conditioning data before analysis.
Democratizing Data Preprocessing with Conversational AI
The traditional approach to data preprocessing creates significant barriers:
- Technical Expertise Required: Complex programming languages and statistical knowledge
- Time-Intensive: Hours or days spent on configuration and testing
- Error-Prone: Manual processes lead to inconsistencies and mistakes
- Limited Accessibility: Only data scientists and analysts can effectively preprocess data
Conversational AI removes these barriers entirely:
- Natural Language Interface: Simply describe what you need in everyday business language
- Instant Results: Preprocessing tasks complete in minutes instead of hours
- Consistent Quality: AI ensures professional-grade results every time
- Universal Access: Anyone can preprocess data, regardless of technical background
Real-World Example:
- Traditional Method: Learn Python/R, configure pandas or scikit-learn, write scripts for missing value imputation, test different normalization approaches, debug errors, document the process (6–8 hours)
- Conversational Method: “Standardize this customer data and fill in missing values using appropriate methods” (5–10 minutes)
Why is Data Preprocessing Important?
The integrity of data analysis is highly dependent on the quality of data preprocessing. Data preprocessing determines the usability and interpretability of data, laying the groundwork for accurate machine learning and AI models.
Eliminating Errors
Cleaning is a pivotal data preprocessing technique. It allows you to eliminate errors, impute missing values, and rectify inconsistencies. With conversational preprocessing, this becomes as simple as saying: “Clean this dataset and fix any quality issues.”
For example, a customer dataset with redundant entries due to technical mistakes would undergo cleaning to ensure each customer record is unique and accurately represented. Instead of writing complex deduplication logic, you can simply request: “Remove duplicate customer records, keeping the most recent version.”
Making Data Uniform
Normalization is comparable to establishing a level playing field, where disparate measures are adjusted to a uniform scale, enabling equitable comparisons. Conversational preprocessing makes this accessible: “Standardize all currency values to USD and normalize the price ranges.”
For instance, normalization can help you analyze the performance of stocks from different countries despite stock prices being available in various currencies and scales. With normalization techniques such as min-max, you can convert all stock prices into a common currency, for example, USD, and then apply a min-max scaling to compare the relative performance of stocks on a uniform scale.
Finding Hidden Patterns
Diligent preprocessing can reveal concealed patterns and insights. A marketing team analyzing social media data can identify peak engagement times aligned with spam activity. However, excluding anomalies through data cleaning will allow you to pinpoint genuine peak engagement periods and optimize strategy.
Big Data Preprocessing
As datasets grow in size and complexity, preprocessing becomes even more critical. Big data has a large volume, is heterogeneous, and needs to be processed rapidly. Preprocessing transforms raw big data into a cleaner, more structured format, removing noise and making it easier to process.
Similarly, advanced techniques such as parallel processing, distributed computing, and automated preprocessing pipelines are indispensable for processing big data effectively.
Data Preparation Has Never Been Easier
Clean, well-prepared data is just a chat away. The only thing Astera Dataprep needs you to do? Have a conversation with it.
Try it Out for Free!How to Preprocess Data Conversationally
Data preprocessing involves several key stages that transform raw data into a format ready for analysis. Each traditional step now has a conversational alternative that makes the process accessible to everyone.
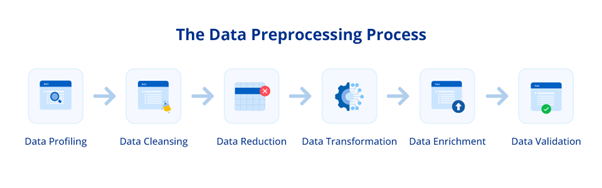
1. Data Profiling
Understanding your data is the first step in preprocessing. Data profiling involves examining the data using summary statistics and distributions to understand its structure, content, and quality. This step can reveal patterns, anomalies, and correlations crucial for informed preprocessing.
Example: A retail manager wants to analyze a dataset of customer purchases to find average spending, most common items, and times of purchase to devise a data-driven marketing strategy. They can simply input the following instruction: “Profile our customer purchase data and identify key spending patterns and trends for marketing strategy.”
2. Data Cleansing
Data cleansing detects and corrects corrupt or inaccurate data records such as errors, outliers, duplicates, and missing values. Methods like imputation for missing data or pruning for outliers help ensure the accuracy of your dataset.
Example: Sales managers correct misspelled product categories or remove duplicate records in sales data. Using chat-based data prep, they can use an instruction such as “Standardize all product categories and remove any duplicate sales records”.
3. Data Reduction
Data reduction aims to decrease the data volume while producing the same or similar analytical results. Techniques like dimensionality reduction, binning, histograms, clustering, and principal component analysis can simplify the data without losing informative patterns and trends.
Example: A researcher only uses the most relevant features from a customer survey to predict buying habits rather than the entire dataset, so they can use the instruction: “Reduce this dataset to the key factors that predict customer behavior”
4. Data Transformation
Data transformation helps modify data for specific needs. It encompasses a variety of steps such as aggregation, normalization, and sorting, among others, each playing a vital role in understanding data.
For example, data aggregation amalgamates individual data points to furnish a consolidated overview, like summarizing monthly sales figures. Similarly, feature creation devises new variables from the existing dataset, which aids in more effectively discerning the intrinsic trends within the data.
Data transformation can also be used to create new attributes within the dataset. You can use mathematical expressions to extract ZIP codes from an address and store them separately or create new attributes from existing features.
Example: A healthcare data analyst leverages mathematical expressions to create new features like Body Mass Index (BMI) through existing features like height and weight. Through conversational data prep, this becomes as easy as writing: “Create BMI values from height and weight data, and extract ZIP codes from addresses”
5. Data Enrichment
Enhancing data with additional sources or derived attributes can provide more depth and context. It involves incorporating demographic information into customer data or adding weather data to sales figures to account for seasonal effects.
Example: A data analyst adds weather data to a retailer’s sales data to see if weather patterns affect buying trends.
6. Data Validation
Before moving on to analysis, it’s crucial to ensure the integrity of your data. Data validation checks that the data meets specific criteria, such as constraints, relations, and ranges. It helps to confirm that the data is accurate, complete, and reliable.
Example: A finance executive checks whether all entries in a transaction dataset fall within expected date ranges and transaction amounts.
Transform your raw data into actionable insights with Astera
Streamline your data preprocessing and processing efforts for visible time and cost savings.
View Demo to See How Astera Can HelpTell Your Data What to Do Instead of Learning Complex Workflows
The fundamental shift from traditional to conversational preprocessing:
Traditional Preprocessing Workflow:
- Learn tool syntax and programming languages
- Research appropriate preprocessing techniques
- Write and test transformation code
- Handle edge cases and errors
- Validate results manually
- Document the process
Total Time: 4–8 hours for basic preprocessing
Conversational Preprocessing Workflow:
- Describe your needs in natural language
- Review AI’s understanding and preview
- Approve the transformation
Total Time: 5–15 minutes for the same preprocessing
Data Preprocessing in Machine Learning: Key Benefits Enhanced by Conversational AI
Ensuring High-Quality Data
Data preprocessing influences the accuracy of analysis directly. Preprocessed data, devoid of irrelevant noise and inconsistencies, allows models to discern and learn from important features, enhancing prediction accuracy and decision-making prowess.
Preprocessing includes several activities, such as cleaning data, handling missing values, normalizing or scaling features, encoding categorical variables, and reducing dimensionality. Each step helps refine the dataset so that the machine learning algorithms can interpret the data correctly and efficiently. For example, understanding how does SVM work is crucial when choosing the right algorithm for classification tasks.
For instance, feature scaling ensures that all the input features have equal weightage, preventing any single feature from disproportionately influencing the model’s output. Similarly, encoding categorical variables into a numerical format is essential for some algorithms that only take numerical data as input.
Refining Model Accuracy and Performance
Preprocessing data in machine learning allows us to remove many obstacles that can hinder model performance. Doing so helps us make more accurate, reliable, and robust predictions.
Preprocessing guards against overfitting, where a model might otherwise internalize the noise as part of the signal, compromising its ability to generalize to new data. Techniques like normalization and feature scaling foster a model’s adaptability.
Feature engineering, an essential facet of model development, is greatly facilitated by preprocessing. It enables innovative features from existing data, refining model performance.
For instance, there’s a medical survey dataset with hundreds of features. Through data preprocessing, particularly feature selection, you can pinpoint the most relevant features—such as age, symptoms, and medical history—that are key to predicting a disease. Doing so discards less important details, like a patient’s favorite color, enhancing the predictive model’s accuracy without modifying the original data.
Accelerate the Learning Process and Model Reliability
The efficiency of the training process also benefits immensely from preprocessing. Algorithms can more swiftly identify patterns in clean data, thus reducing the time, effort, and energy spent training the algorithm. All these are vital considerations in big data environments.
Furthermore, the reliability of insights gleaned from AI and machine learning hinges on the precision of preprocessing. It ensures the data input into models is trustworthy, enabling dependable and actionable predictions.
How Chat-Based Data Preprocessing Simplifies Traditional Techniques
Data preprocessing techniques help you fine-tune data for machine learning models or statistical analysis. With conversational AI, these complex techniques become as simple as describing what you need:
Data Imputation
Missing data can skew analysis and lead to inaccurate models. Strategies for handling missing values include imputation (filling in missing values with statistical measures like mean or median) or using algorithms that can handle missing data, such as random forests.
Reduce Noisy Data
Noisy data can obscure meaningful patterns. Techniques like smoothing (using rolling averages) and filtering (applying algorithms to remove noise) help clarify the signal in data. For instance, a moving average can smooth out short-term fluctuations and highlight longer-term trends.
Identify and Remove Duplicates
Duplicate data can distort analysis, leading to biased results. Detection can be as simple as searching for identical records or as complex as identifying near-duplicates using fuzzy matching. Removal ensures each data point is unique, maintaining the integrity of your dataset.
Feature Engineering
Creating new features from existing data can unlock profound insights. This process might involve combining two variables to create a new one, such as calculating the Body Mass Index from weight and height or extracting parts of data (like the day of the week) for time series analysis.
Feature Scaling or Normalization
Scaling features to a uniform range ensures that no single feature dominates the model due to scale. Methods include min-max scaling, which rescales the feature to a fixed range, usually 0 to 1, or standardization, which centers the feature on zero with unit variance.
Dimensionality Reduction
Dimensionality reduction techniques, like Principal Component Analysis, lower the variables under consideration, simplifying the model without losing significant information. This method can improve model performance and reduce computational complexity.
Discretization
Converting continuous features into discrete bins can make the data more manageable and improve model performance. For example, age can be binned into categories like ’18-25′, ’26-35′, etc., to simplify analysis and reveal generational trends.
Feature Encoding
Categorical data encoding methods, such as one-hot or label encoding, convert categorical variables into numerical form for model training. Encoding is essential for algorithms that require numerical input.
Enjoy up to 60% time savings. Optimize your data preprocessing with Astera.
Simplify your data preparation with our comprehensive, step-by-step guide.
Download the data prep guide for free.Data Preprocessing Tools + The Chat-Based Advantage
Data preprocessing tools simplify how you interact with extensive data, making it easier to shape and polish complex data. However, conversational AI represents the next evolution, making all preprocessing tasks accessible through natural language.
Traditional Tools:
- Pandas: This Python library offers a wide array of functions for handling data, making it ideal for cleaning, filtering, and aggregating large datasets.
- Scikit-learn: Scikit-learn is equipped to handle everything from feature scaling to encoding categorical variables, ensuring your data is in the best shape for modeling.
- OpenRefine: Designed for the challenges of messy data, OpenRefine is a standalone tool that cleans and transforms data. It’s beneficial for standardizing data formats and enriching datasets with information from external sources.
Chat-Based Data Preprocessing Advantages:
- Zero Learning Curve: No programming or technical training required
- Natural Language Interface: Describe what you need in everyday business language
- Instant Results: Complex preprocessing tasks complete in minutes
- Professional Quality: AI ensures enterprise-grade results consistently
- Universal Access: Anyone can preprocess data, regardless of background
pandas.dropna(), fillna()StandardScaler().fit_transform()pd.get_dummies()SimpleImputer()How Astera Dataprep Streamlines Data Preprocessing
Astera Dataprep simplifies data preprocessing by eliminating the traditional barriers of technical expertise and coding proficiency. Its chat-based interface ensures that preprocessing meets users where they are and speaks their language — and offers plenty of other benefits too.
- Speed: Accelerate the data preparation process from hours to minutes with conversational AI, delivering faster insights. Simply describe what you need: “Prepare this customer data for churn analysis” → Complete preprocessing in under 15 minutes
- Accuracy: Minimize human error with AI-powered interpretation of natural language requirements. Traditional manual processes are replaced by consistent, professional-grade automation
- Accessibility: Anyone can preprocess data by describing their needs in plain English. No technical training, coding knowledge, or specialized personnel required
- Cost-Efficiency: Reduce the need for specialized personnel and training by making data preprocessing accessible to business users, analysts, and domain experts
- Agility: Quickly adapt to changing data requirements with conversational flexibility – just describe new requirements and AI handles the technical implementation
- Scalability: Effortlessly handle growing data volumes and complexity through cloud-native conversational processing that scales automatically
Real-World Chat-Based Preprocessing Examples
Business User: “I need this sales data cleaned up and ready for monthly reporting”
AI Response: Automatically removes duplicates, standardizes formats, handles missing values, and creates monthly aggregations
Data Analyst: “Prepare this customer survey data for machine learning, focusing on churn prediction”
AI Response: Applies feature engineering, encoding, scaling, and validation optimized for churn models
Marketing Manager: “Enrich our customer data with demographic information and segment by purchase behavior”
AI Response: Connects to data sources, performs enrichment, and creates behavioral segments
The Astera Advantage
Astera Dataprep’s user-friendly platform democratizes the data preparation process with conversational, cloud-based data preprocessing, enabling you to describe your needs in natural language while AI handles automated data collection, cleaning, transformation, and organization regardless of technical expertise.
Ready to transform your data preprocessing workflow? Experience Astera Dataprep firsthand by signing up for a 14-day free trial.
What is data preprocessing in machine learning?
Why is data preprocessing important?
What are the main steps involved in conventional data preprocessing?
The primary steps in conventional data preprocessing include:
- Data Profiling: Understanding the structure and quality of the data.
- Data Cleansing: Correcting errors and handling missing values.
- Data Reduction: Simplifying the dataset by reducing its size without losing significant information.
- Data Transformation: Modifying data to fit analytical needs, such as normalization or aggregation.
- Data Enrichment: Enhancing data by adding relevant information from external sources.
- Data Validation: Ensuring the data meets specific criteria and is ready for analysis.
How does data preprocessing differ from data cleaning?
What techniques are commonly used in data preprocessing?
Common data preprocessing techniques include:
- Data Imputation: Filling in missing values using statistical methods.
- Noise Reduction: Smoothing out irregularities in the data to highlight important patterns.
- Feature Scaling: Adjusting the scale of variables to ensure uniformity.
- Encoding Categorical Variables: Converting categorical data into numerical formats for analysis.
- Dimensionality Reduction: Reducing the number of variables under consideration to simplify models.
What tools can assist with data preprocessing?
Several tools can facilitate data preprocessing, including:
- Pandas: A Python library offering functions for data manipulation and analysis.
- Scikit-learn: Provides utilities for preprocessing tasks like scaling and encoding.
- OpenRefine: A tool designed for cleaning and transforming messy data.
- Astera Dataprep: Streamlines data preprocessing with a chat-based interface and support for natural language instructions, enabling users to simply describe their needs while AI handles automated data collection, cleaning, transformation, and organization without any coding or technical training required.
How does conversational AI change data preprocessing?
Conversational AI democratizes data preprocessing by:
- Eliminating technical barriers – anyone can preprocess data using natural language
- Reducing time from hours to minutes – describe needs instead of configuring tools
- Ensuring consistent quality – AI applies best practices automatically
- Making expertise accessible – business users get data scientist-level results
- Enabling collaboration – teams work together using common business language