The 13 Best Data Mapping Tools in 2026 For No-Code/Low-Code Data Mapping
Managing data effectively is a multi-layered activity—you must carefully locate it, consolidate it, and clean it to make it usable. And one of the first steps in the data management cycle is data mapping, which is the process of defining how data elements in one system or format correspond to those in another.
Data mapping tools have emerged as a powerful solution to help organizations make sense of their data, facilitating data integration, improving data quality, and enhancing decision-making processes. Analyst firm valued dedicated data mapping software at roughly US $1.5 billion in 2023, forecasting they will reach US $4.2 billion by 2032, a solid 12.4 % CAGR. That expansion parallels the wider data integration software space, which Cognitive Market Research sizes at US $15.24 billion for 2024 with a projected 12.31 % annual growth through 2031.
Together these figures show that mapping has graduated from a bolt-on feature to a core pillar of the integration stack—one that enterprises are now funding explicitly as they race to make ever-growing data streams analytics-ready. However, choosing the data mapping platform that fits your data architecture, governance requirements, and budget is easier said than done, especially when the options range from full-stack integration suites with built-in mapping to focused, best-of-breed standalone tools.
In this article, we will list 2026’s top data mapping tools with their key features and offer expert advice on how you should select the right one for your business.
- Core role of mapping: Data mapping defines how source fields correspond to target fields, ensuring that data retains context and structure when moved between systems.
- AI-driven automation: Modern platforms like Astera use AI chatbots to suggest and create mappings through natural language instructions, reducing manual effort and improving accuracy.
- Validation is critical: Mapping tools include validation rules to flag schema mismatches and ensure data quality before integration.
- Wide integration use‑cases: Data mapping is used across ETL, data migration, BI, integration, and data warehousing to align diverse data sources.
- Visual & no-code interfaces: Many tools let users drag‑and‑drop mappings, making mapping accessible without writing transformation code.
- Schema flexibility: Astera Centerprise supports dynamic layouts, so if your source schema changes (e.g. new columns), mappings automatically adapt.
- Scalable ETL engine: Astera’s engine is built for high-performance, parallel processing, enabling mapping at scale with large datasets.
- Extensive connectivity: Centerprise supports built-in and custom connectors, making it possible to map data across on-prem, cloud, and hybrid environments.
- Drag‑and‑drop transformations: Astera provides built-in transformation functions (e.g., merging, lookup, conversion) so mapping isn’t just one-to-one—it’s intelligent.
- Proven recognition: Centerprise is recognized on G2 as a strong player in both ETL and data mapping, highlighting its mapping capabilities.
What is Data Mapping?
Data mapping defines how data from a source system corresponds to fields or structures in a target system. It provides the instructions that allow information to move correctly between environments with different schemas or conventions. Without mapping, data transferred across systems loses its context or becomes misaligned.
The data-mapping process typically begins with an analysis of both the source and target schemas. For instance, customer contact details scattered across several tables in a legacy system must be consolidated into a single JSON object so the modern application can load it into the new platform’s customer-profile schema and make it available to downstream services. The mapping step then determines how to reshape and reorganize the data to achieve that structure.
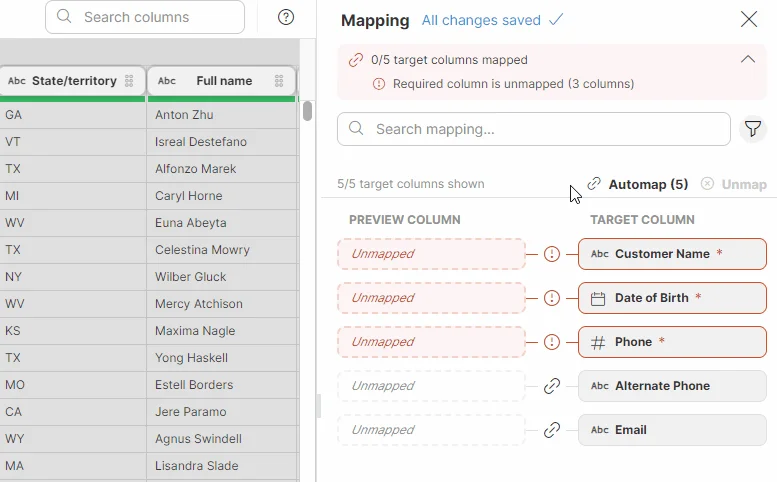
Modern data mapping tools automate much of this consolidation by letting you drag-and-drop source fields onto target fields while generating the necessary transformation logic at the backend. Built-in validation rules flag any mismatches to ensure the converted data is consistent and ready for analytics.
AI in Data Mapping
Advanced data integration platforms, like Astera, also provide artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to automate the data mapping process. Instead of manually pairing each field or writing transformation rules by hand, you take advantage of AI to get mapping recommendations and automatically map fields based on schema analysis. AI data mapping is a highly sought-after feature these days, and is particularly useful when dealing with unknown or frequently changing data sources. It also facilitates customizable transformations by merging columns, creating nested records, and computing arithmetic values while mapping your data.
The Role of Automated Data Mapping Features in Data Integration
When you move data from one system to another, you must shape it to fit the structure and semantics expected by the destination system. This is called interoperability and is what data mapping capabilities found in data integration platforms enable. Data mapping tools allow businesses to break down data silos as they combine data from multiple sources to create a unified view of their operations. Another benefit of data mapping in a data integration pipeline is improved data quality management. Accurate mapping ensures that the integrated data is accurate and consistent.
What are Data Mapping Tools?
Data mapping tools are software applications or platforms that simplifies and automates the process of specifying how each element of one data set corresponds to an element in another data set. To support that process, these tools provide validation and profiling features that identify mapping errors and maintain audit trail for each transformation rule.
The goal with data mapping tools is to ensure that every element in the source finds its exact counterpart in the target. To achieve this, modern platforms offer a visual or declarative interface. Data mapping tools are used to:
- Discover and align the schemas of source and target systems
- Define and apply transformation rules for format and value conversion
- Ensure data types convert correctly and values remain accurate
- Enforce business logic such as lookups, defaults, and conditional rules
- Validate that every required field is mapped and relationships stay intact
- Document mappings for review and ongoing maintenance
- Run the mapping as part of an automated workflow or batch job
Data mapping tools are commonly used for following use cases and processes:
- ETL (extract, transform, load)
- Data warehousing
- Business intelligence
- Data migration
- Application integration
Top 13 Data Mapping Tools in 2026
Whether you are a small startup or a large enterprise, finding the right data mapping tool is essential for data management. Below is a list of 13 data mapping tools:
1. Astera
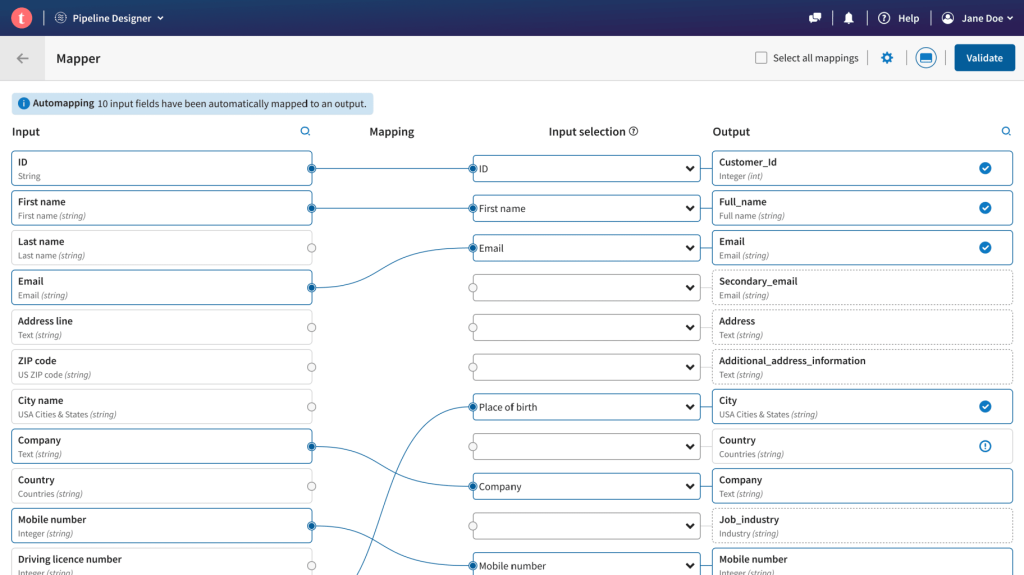
Astera is an enterprise-grade, cloud-based data management platform that offers organizations various no-code solutions in a unified data stack, including AI-powered data extraction, data preparation, integration, EDI, data warehousing, and API management.
As a data mapping tool, Astera offers AI-driven semantic mapping, which automatically maps and aligns data fields across disparate sources and destinations, considerably reducing manual effort and increasing accuracy.
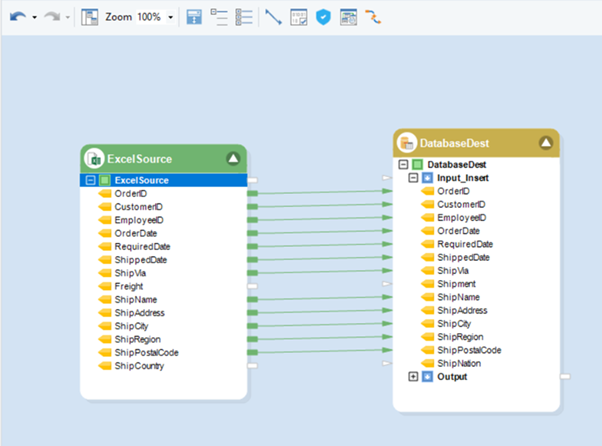
Moreover, Astera’s industrial strength ETL engine allows seamless integration with various data sources and destinations, including databases, cloud platforms, and APIs, making it easier for organizations to extract, integrate, and manipulate data efficiently. Its AI-powered automation and orchestration features reduce the time needed to manage ETL processes by as much as 80%.
Key Features
- AI-powered semantic mapping
- Cloud-based, AI-powered data preparation
- Unified data pipeline creation
- No-code, visual user interface
- Rich data transformations
- Industrial strength ETL engine
- Process orchestration with workflow automation and job scheduling
- Support for all data latencies (real-time, near-real-time, batch data)
- Advanced data quality features
- 100+ connectors for multiple on-premises and cloud-based sources with API integrations
Astera's AI-powered solution not only maps your data but ensures end-to-end data integration. Leverage our unified platform to make the most of your data. The Right Data Integration Platform Can Change The Game
2. Ketch

Ketch is a privacy-first data mapping platform that automates the discovery, classification, and governance of personal data across cloud, SaaS, and on-premises systems.
As a data mapping tool, Ketch employs AI-powered system discovery to identify and classify personal data across your organization. It provides real-time visibility into data flows, enabling efficient privacy operations and compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Key Features
- AI-powered system discovery
- Metadata-based data classification
- Real-time data flow visualization
- Automated ROPA generation
- Consent and rights integration
- Risk assessment and mitigation tools
- 400+ pre-built connectors
- Centralized policy management
3. Talend
Talend is a cloud-based data integration tool with data mapping capabilities. It provides connectivity to various sources, including multiple file formats and databases. The tool is low-code, which means users will need to write scripts..
Talend also provides features, such as batch processing, for data mapping across bigger data sets.
Key Features
- Low-code
- Data Profiling
- Pre-built Connectors
- Big Data Compatibility.
- Data cleansing functionalities before loading data into a warehouse.
4. Informatica
Informatica offers a low-code data management and mapping tool. It allows users to define reusable data flow logic for mapping datasets.
The low code functionality of the tool means that users might have to write code for complex transformations.
Key Features
- Low-code
- AI-powered Tool.
- Re-usable Scripts and Dynamic Mapping.
- Built-in Connectors
- Workflow Automation
5. Dell Boomi
Dell Boomi is a cloud-based data mapping and integration solution. Users can use its point-and-click interface and pre-built connectors to map a source system to a destination.
Key Features
- Low-code tool
- Workflow automation
- Intelligent data mapping suggestions
- Pre-built connectors
- Custom logic through data map extensions.
- Field-locking to enforce certain standards.
6. Mulesoft Anypoint
MuleSoft Anypoint is a cloud-based integration platform (iPaaS) that provides organizations with a platform for building and managing their APIs and integrations. The tool has data transformation capabilities allowing users to map data between different file formats and protocols.
Key Features
- Low code tool
- Real-time Error Handling
- Advanced Security
- Multiple transformations
- Automapping between same-structure schemas.
7. Pentaho
Pentaho is a data integration and business analytics platform that enables enterprises to collect, prepare, blend, and analyze data from various sources. It provides a set of tools for data mapping, ETL, data warehousing, mining, and reporting. Pentaho allows users to create and manage complex data mappings visually.
Key Features
- Connectors for databases, flat files, and cloud sources.
- Re-usable scripts for data mapping
- Real-time error detection
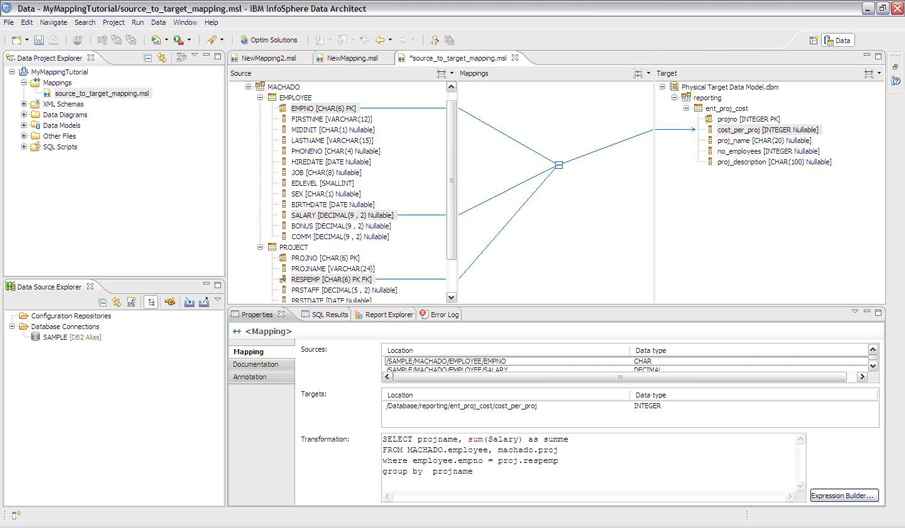
8. IBM InfoSphere
IBM InfoSphere is a data management solution with data mapping capabilities. The tool uses the Mapping Assist functionality for object mapping and workflow creation.
Key Features
- Self-learning model for improving mapping accuracy with each new task.
- Intelligent JSON-format transformation suggestions.
- Compatible with Big data sources.
9. Jitterbit
Jitterbit is a low-code data mapping platform as a service that allows businesses to connect their applications and data, automate business processes, and create new digital experiences. It also lets users to create ETL pipelines and perform data migration. Jitterbit is also deployable on the cloud.
Key Features
- Automapping.
- Condition-based mapping.
- Loop node mapping for hierarchical structures.
- Connectivity with various CRM and accounting systems.
- Point and click interface for easy mapping and transformations.
10. CloverDX
CloverDX is an open-source enterprise data management platform that allows businesses to integrate, transform, and manage their data. It provides a set of tools which includes data mapping, data migration, data warehousing, and data quality management.
Key Features
- Drag-and-drop interface.
- Flexibility of creating both code-based and no-code mappings.
- Expression-based mapping.
- Free alternative to other options on this list.
- Parallel processing.
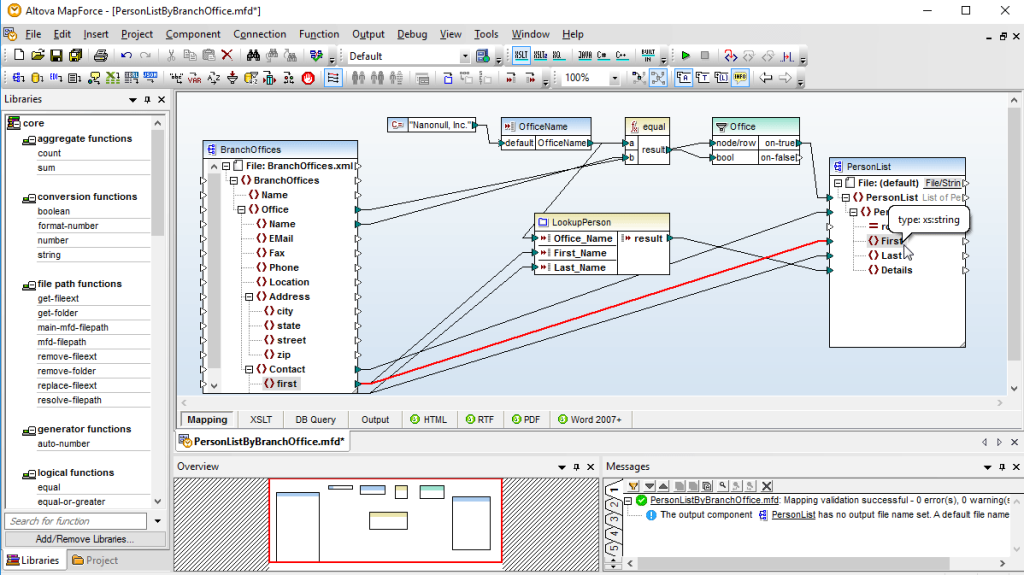
11. Altova MapForce
Altova MapForce is a graphical data mapping tool for any-to-any conversion and integration. It supports a wide range of data formats, including XML, JSON, databases, EDI, Excel, XBRL, and Web services. Altova MapForce can be used to build data integration and conversion applications, as well as to automate recurring data transformations.
Key Features
- Interactive data mapping debugger.
- A library of built-in data mapping functions.
- Extensive data source support.
- Chained data mappings.
- Data mapping output preview.
- Automation and job-scheduling.
12. Skyvia
Skyvia is a cloud-based data integration platform that allows users to connect to and integrate data from multiple sources, including cloud applications, relational databases, and CSV files. Skyvia provides various data mapping features so users can transform their data into the format required by their target destination.
Key Features
- No-code visual interface.
- Advanced mappings, including column and relation mapping.
- Mapping in synchronization.
- A mapping editor.
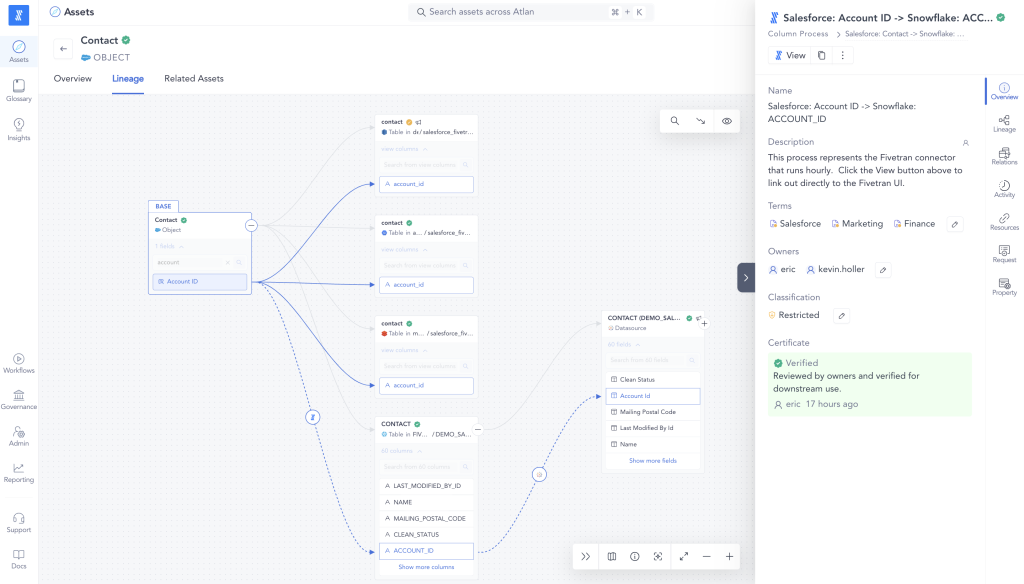
13. Fivetran
Fivetran is a fully managed data pipeline platform allowing companies to connect and sync their data from various sources to popular cloud data warehouses and analytics destinations. It automates the data pipeline process, allowing companies to get their data into the cloud and use it to power their businesses.
Key Features
- Pre-built and custom transformations.
- Cloud deployment.
- Automated and custom data mapping.
- Automatic schema migrations.
What To Look For In Data Mapping Tools When Making a Purchase Decision
Effective data mapping tools possess certain key features that make them invaluable to businesses. These features ensure that the data mapping process is efficient, accurate, and reliable:
- Intuitive User Interface: A user-friendly interface ensures data mapping is a straightforward and streamlined process, even for users with limited technical expertise. Business users can easily define mapping rules, transform data, and validate mappings.
- Data Compatibility: Top data mapping tools support various data formats, including XML, CSV, JSON, and more, allowing you to integrate multiple systems and applications without compatibility issues.
- Advanced Mapping Capabilities: Data mapping tools offer advanced mapping functionalities, such as conditional mapping, transformation rules, and automated data validation. These capabilities enable businesses to handle complex data mapping scenarios and ensure data accuracy and consistency. Plus, as these tools integrate AI, automated mapping will become the new norm.
- Data Governance: Data mapping tools provide features for data governance, including version control and data quality monitoring. These features help businesses maintain data integrity, track data changes, and ensure compliance with data governance policies and regulations.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating existing systems, databases, and applications is crucial for seamless data mapping implementation. Effective data mapping tools offer integration capabilities that allow businesses to connect and map data between different systems, ensuring smooth data flow and synchronization.
- Instant Data Mapping Preview: Modern data mapping tools enable you to see how your data will change in real-time in the design stage, ensuring it’s accurate and error-free before proceeding.
Map your data effortlessly with Astera's AI-Driven Semantic Mapping
Let AI map all your sources to the correct destinations for smooth and effortless data integration. Astera's AI-powered semantic data mapping makes data integration easier than ever.
Connect with us for a free trial or a personalized demo.Choosing the Right Data Mapping Tool for Your Needs
With several data mapping solutions available, choosing the right one for your business can be challenging. However, you can make an informed decision by considering some key factors.
Assess Your Business’s Data Mapping Needs
Start by assessing your business’s specific data mapping requirements. Consider the types of data sources you need to integrate, the complexity of your data transformations, and the level of technical expertise within your team. For example, if your business deals with various data sources, such as databases, APIs, and flat files, you will need a data mapping tool that supports multiple data formats.
Furthermore, consider the scalability of the tool. As your business grows, your data mapping needs may evolve. Choose a tool that can accommodate future requirements and handle increasing data volumes.
Compare Costs and Features of Different Tools
Compare the costs and features of different data mapping software. Evaluate pricing models, including licensing fees and ongoing maintenance costs. You should also consider the long-term costs associated with the tool and any additional expenses for training and support.
Additionally, carefully review the features and functionalities offered by each tool and determine which ones align best with your business requirements. Some common features to consider include data validation, data enrichment, and data transformation capabilities. Look for tools that offer intuitive user interfaces and provide comprehensive documentation.
Implementing Data Mapping Tools in Your Business
Once you have chosen the right data mapping tool for your needs, it’s time to implement it effectively in your business processes.
Implementing data mapping tools requires careful planning and execution. Here are some steps to help you successfully integrate a data mapping tool into your organization:
- Identify Integration Points: Determine the applications and systems that need to be integrated with the data mapping tool.
- Define Mapping Requirements: Clearly define your data mapping requirements, including data formats, transformation rules, and validation criteria.
- Configure the Tool: Set up the data mapping tool according to your specific requirements, including mapping connections and transformation rules.
- Test and Validate: Conduct thorough testing and validation to ensure that the data mapping tool functions correctly and meets your integration goals.
- Train Users: Provide comprehensive training to your team members to ensure they can use the data mapping tool proficiently.
Businesses may encounter certain challenges. Understanding these challenges and taking proactive measures can significantly contribute to accurate data mapping.
- Complex Data Structures: Dealing with complex data structures can pose challenges during mapping. It is crucial to analyze data structures and plan the mapping accordingly carefully. You can simplify mapping and ensure accurate data transformation by breaking down complex data structures into manageable components.
- Data Validation: Ensuring data accuracy and integrity is vital. Implementing appropriate data validation mechanisms can help identify and address any inconsistencies or errors in the data. By performing data validation checks at various stages of the mapping process, you can minimize the risk of data corruption and ensure the reliability of your mapped data.
- Change Management: Implementing a data mapping tool may require changes in existing processes and workflows. Effective change management practices can help smooth the transition and gain user acceptance. By involving key stakeholders early in the implementation process, providing clear communication and training, and addressing any concerns or resistance, you can facilitate a smooth transition and ensure successful adoption of the data mapping tool.
Conclusion
Data mapping tools are crucial in simplifying data integration and transformation. By accurately linking data elements between systems, organizations can view data comprehensively, enhance its quality, and make informed decisions.
Astera, with its AI-powered features, intuitive interface, and extensive connectivity options, emerges as a top choice for organizations from among the data integration tools listed above.
Experience how Astera’s AI-powered data mapping tool can make your data integration tasks easier and quicker. Download our 14-day free trial, or sign up for a free demo today!